Continuous Subarray Sum Python Dynamic Programming
Given an array arr[] of size N. The task is to find the sum of the contiguous subarray within a arr[] with the largest sum.
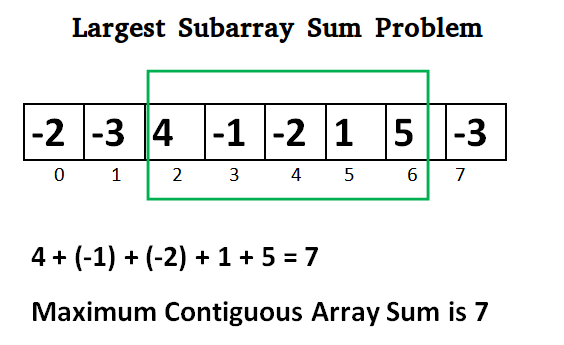
Kadane's Algorithm:
The idea of Kadane's algorithm is to maintain a variable max_ending_here that stores the maximum sum contiguous subarray ending at current index and a variable max_so_far stores the maximum sum of contiguous subarray found so far, Everytime there is a positive-sum value in max_ending_here compare it with max_so_far and update max_so_far if it is greater than max_so_far.
Pseudocode :
Initialize:
max_so_far = INT_MIN
max_ending_here = 0Loop for each element of the array
(a) max_ending_here = max_ending_here + a[i]
(b) if(max_so_far < max_ending_here)
max_so_far = max_ending_here
(c) if(max_ending_here < 0)
max_ending_here = 0
return max_so_far

Illustration:
Lets take the example: {-2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3}
max_so_far = INT_MIN
max_ending_here = 0for i=0, a[0] = -2
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (-2)
Set max_ending_here = 0 because max_ending_here < 0
and set max_so_far = -2for i=1, a[1] = -3
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (-3)
Since max_ending_here = -3 and max_so_far = -2, max_so_far will remain -2
Set max_ending_here = 0 because max_ending_here < 0for i=2, a[2] = 4
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (4)
max_ending_here = 4
max_so_far is updated to 4 because max_ending_here greater
than max_so_far which was -2 till nowfor i=3, a[3] = -1
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (-1)
max_ending_here = 3for i=4, a[4] = -2
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (-2)
max_ending_here = 1for i=5, a[5] = 1
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (1)
max_ending_here = 2for i=6, a[6] = 5
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (5)
max_ending_here = 7
max_so_far is updated to 7 because max_ending_here is
greater than max_so_farfor i=7, a[7] = -3
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (-3)
max_ending_here = 4
Note: The above algorithm only works if and only if at least one positive number should be present otherwise it does not work i.e if an Array contains all negative numbers it doesn't work.
Follow the below steps to Implement the idea:
- Initialize the variables max_so_far = INT_MIN and max_ending_here = 0
- Run a for loop form 0 to N-1 and for each index i:
- Add the arr[i] to max_ending_here.
- If max_so_far is less than max_ending_here then update max_so_far to max_ending_here.
- If max_ending_here < 0 then update max_ending_here = 0
- Return max_so_far
Below is the Implementation of above approach.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int maxSubArraySum( int a[], int size)
{
int max_so_far = INT_MIN, max_ending_here = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + a[i];
if (max_so_far < max_ending_here)
max_so_far = max_ending_here;
if (max_ending_here < 0)
max_ending_here = 0;
}
return max_so_far;
}
int main()
{
int a[] = { -2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3 };
int n = sizeof (a) / sizeof (a[0]);
int max_sum = maxSubArraySum(a, n);
cout << "Maximum contiguous sum is " << max_sum;
return 0;
}
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Kadane {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int [] a = { - 2 , - 3 , 4 , - 1 , - 2 , 1 , 5 , - 3 };
System.out.println( "Maximum contiguous sum is "
+ maxSubArraySum(a));
}
static int maxSubArraySum( int a[])
{
int size = a.length;
int max_so_far = Integer.MIN_VALUE, max_ending_here
= 0 ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) {
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + a[i];
if (max_so_far < max_ending_here)
max_so_far = max_ending_here;
if (max_ending_here < 0 )
max_ending_here = 0 ;
}
return max_so_far;
}
}
Python
from sys import maxint
def maxSubArraySum(a, size):
max_so_far = - maxint - 1
max_ending_here = 0
for i in range ( 0 , size):
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + a[i]
if (max_so_far < max_ending_here):
max_so_far = max_ending_here
if max_ending_here < 0 :
max_ending_here = 0
return max_so_far
a = [ - 2 , - 3 , 4 , - 1 , - 2 , 1 , 5 , - 3 ]
print "Maximum contiguous sum is" , maxSubArraySum(a, len (a))
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static int maxSubArraySum( int [] a)
{
int size = a.Length;
int max_so_far = int .MinValue, max_ending_here = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + a[i];
if (max_so_far < max_ending_here)
max_so_far = max_ending_here;
if (max_ending_here < 0)
max_ending_here = 0;
}
return max_so_far;
}
public static void Main()
{
int [] a = { -2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3 };
Console.Write( "Maximum contiguous sum is "
+ maxSubArraySum(a));
}
}
PHP
<?php
function maxSubArraySum( $a , $size )
{
$max_so_far = PHP_INT_MIN;
$max_ending_here = 0;
for ( $i = 0; $i < $size ; $i ++)
{
$max_ending_here = $max_ending_here + $a [ $i ];
if ( $max_so_far < $max_ending_here )
$max_so_far = $max_ending_here ;
if ( $max_ending_here < 0)
$max_ending_here = 0;
}
return $max_so_far ;
}
$a = array (-2, -3, 4, -1,
-2, 1, 5, -3);
$n = count ( $a );
$max_sum = maxSubArraySum( $a , $n );
echo "Maximum contiguous sum is " ,
$max_sum ;
?>
Javascript
<script>
function maxSubArraySum(a, size)
{
var maxint = Math.pow(2, 53)
var max_so_far = -maxint - 1
var max_ending_here = 0
for ( var i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + a[i]
if (max_so_far < max_ending_here)
max_so_far = max_ending_here
if (max_ending_here < 0)
max_ending_here = 0
}
return max_so_far
}
var a = [ -2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3 ]
document.write( "Maximum contiguous sum is" ,
maxSubArraySum(a, a.length))
</script>
Output
Maximum contiguous sum is 7
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Print the Largest Sum Contiguous Subarray
To print the subarray with the maximum sum the idea is to maintain start index of maximum_sum_ending_here at current index so that whenever maximum_sum_so_far is updated with maximum_sum_ending_here then start index and end index of subarray can be updated with start and current index.
Follow the below steps to implement the idea:
- Initialize the variables s, start, and end with 0 and max_so_far = INT_MIN and max_ending_here = 0
- Run a for loop form 0 to N-1 and for each index i:
- Add the arr[i] to max_ending_here.
- If max_so_far is less than max_ending_here then update max_so_far to max_ending_here and update start to s and end to i .
- If max_ending_here < 0 then update max_ending_here = 0 and s with i+1.
- Print values from index start to end.
Below is the Implementation of above approach:
C++
#include <climits>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void maxSubArraySum( int a[], int size)
{
int max_so_far = INT_MIN, max_ending_here = 0,
start = 0, end = 0, s = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
max_ending_here += a[i];
if (max_so_far < max_ending_here) {
max_so_far = max_ending_here;
start = s;
end = i;
}
if (max_ending_here < 0) {
max_ending_here = 0;
s = i + 1;
}
}
cout << "Maximum contiguous sum is " << max_so_far
<< endl;
cout << "Starting index " << start << endl
<< "Ending index " << end << endl;
}
int main()
{
int a[] = { -2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3 };
int n = sizeof (a) / sizeof (a[0]);
int max_sum = maxSubArraySum(a, n);
return 0;
}
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static void maxSubArraySum( int a[], int size)
{
int max_so_far = Integer.MIN_VALUE,
max_ending_here = 0 , start = 0 , end = 0 , s = 0 ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) {
max_ending_here += a[i];
if (max_so_far < max_ending_here) {
max_so_far = max_ending_here;
start = s;
end = i;
}
if (max_ending_here < 0 ) {
max_ending_here = 0 ;
s = i + 1 ;
}
}
System.out.println( "Maximum contiguous sum is "
+ max_so_far);
System.out.println( "Starting index " + start);
System.out.println( "Ending index " + end);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a[] = { - 2 , - 3 , 4 , - 1 , - 2 , 1 , 5 , - 3 };
int n = a.length;
maxSubArraySum(a, n);
}
}
Python3
from sys import maxsize
def maxSubArraySum(a, size):
max_so_far = - maxsize - 1
max_ending_here = 0
start = 0
end = 0
s = 0
for i in range ( 0 , size):
max_ending_here + = a[i]
if max_so_far < max_ending_here:
max_so_far = max_ending_here
start = s
end = i
if max_ending_here < 0 :
max_ending_here = 0
s = i + 1
print ( "Maximum contiguous sum is %d" % (max_so_far))
print ( "Starting Index %d" % (start))
print ( "Ending Index %d" % (end))
a = [ - 2 , - 3 , 4 , - 1 , - 2 , 1 , 5 , - 3 ]
maxSubArraySum(a, len (a))
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static void maxSubArraySum( int [] a, int size)
{
int max_so_far = int .MinValue, max_ending_here = 0,
start = 0, end = 0, s = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
max_ending_here += a[i];
if (max_so_far < max_ending_here) {
max_so_far = max_ending_here;
start = s;
end = i;
}
if (max_ending_here < 0) {
max_ending_here = 0;
s = i + 1;
}
}
Console.WriteLine( "Maximum contiguous "
+ "sum is " + max_so_far);
Console.WriteLine( "Starting index " + start);
Console.WriteLine( "Ending index " + end);
}
public static void Main()
{
int [] a = { -2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3 };
int n = a.Length;
maxSubArraySum(a, n);
}
}
PHP
<?php
function maxSubArraySum( $a , $size )
{
$max_so_far = PHP_INT_MIN;
$max_ending_here = 0;
$start = 0;
$end = 0;
$s = 0;
for ( $i = 0; $i < $size ; $i ++)
{
$max_ending_here += $a [ $i ];
if ( $max_so_far < $max_ending_here )
{
$max_so_far = $max_ending_here ;
$start = $s ;
$end = $i ;
}
if ( $max_ending_here < 0)
{
$max_ending_here = 0;
$s = $i + 1;
}
}
echo "Maximum contiguous sum is " .
$max_so_far . "\n" ;
echo "Starting index " . $start . "\n" .
"Ending index " . $end . "\n" ;
}
$a = array (-2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3);
$n = sizeof( $a );
$max_sum = maxSubArraySum( $a , $n );
?>
Javascript
<script>
function maxSubArraySum(a , size) {
var max_so_far = Number.MIN_VALUE, max_ending_here = 0, start = 0, end = 0, s = 0;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
max_ending_here += a[i];
if (max_so_far < max_ending_here) {
max_so_far = max_ending_here;
start = s;
end = i;
}
if (max_ending_here < 0) {
max_ending_here = 0;
s = i + 1;
}
}
document.write( "Maximum contiguous sum is " + max_so_far);
document.write( "<br/>Starting index " + start);
document.write( "<br/>Ending index " + end);
}
var a = [ -2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3 ];
var n = a.length;
maxSubArraySum(a, n);
</script>
Output
Maximum contiguous sum is 7 Starting index 2 Ending index 6
Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Kadane's Algorithm can be viewed both as greedy and DP. As we can see that we are keeping a running sum of integers and when it becomes less than 0, we reset it to 0 (Greedy Part). This is because continuing with a negative sum is way worse than restarting with a new range. Now it can also be viewed as a DP, at each stage we have 2 choices: Either take the current element and continue with the previous sum OR restart a new range. Both choices are being taken care of in the implementation.
Practice Problem:
Given an array of integers (possibly some elements negative), write a C program to find out the *maximum product* possible by multiplying 'n' consecutive integers in the array where n ≤ ARRAY_SIZE. Also, print the starting point of the maximum product subarray.
Please write comments if you find anything incorrect, or if you want to share more information about the topic discussed above.
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/largest-sum-contiguous-subarray/
0 Response to "Continuous Subarray Sum Python Dynamic Programming"
ارسال یک نظر